2023 was a real inflection point in the realm of cybersecurity and cybercrime. While the year saw companies give more importance to the role of cybersecurity in their organization, the fact of the matter is that cybercrime continued to be on the rise. The average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, highlighting a 15% increase over the last three years. In addition, Statista also reported that 72.7% of all organizations fell prey to a ransomware attack in 2023.
To that end, Gartner recently identified the top 6 cybersecurity trends that will shape 2024 – a great read, if you haven’t checked it out already. What we wanted to do was bring to light several cautionary tales that occurred in 2023, and how each incident’s learnings are linked to Gartner’s 6 trends for 2024.
Trend #1: Turning short-term skepticism for Generative AI into long-term hope
Generative AI is a relatively new technology, and all of those tend to have teething problems.
Last year, Samsung banned the use of ChatGPT and other AI-powered chatbots because of how precariously 3 different employees used it:
- One engineer entered source code to find out how to resolve a software bug.
- One executive recorded a confidential meeting, used a transcribing software and fed it to ChatGPT to conjure up meeting notes.
- A third employee used it to optimize the test sequence for identifying defective chips.
The tricky part is, that once this data is fed, it gets stored on those servers with no easy way to access and delete them. Furthermore, prior conversations are used to train these AI models, so there’s every chance that your sensitive data could be served up to other users.
Therefore, through proactive collaboration with business stakeholders, organizations must build the foundations for ethical, safe, and secure usage of this highly disruptive tech. Encourage experimentation and manage expectations, especially when it comes to employees outside your security team so that they know the power (and danger) of these transformative tools. Incidents like the Samsung-ChatGPT one will continue to pop up, yet that shouldn’t distract from the ultimate fact that AI could be transformative for both your business operations and your cybersecurity strategy.
Trend #2: The Rise of Cybersecurity Outcome-Driven Metrics (ODMs)
Incidents like the aforementioned scenario bring relevance to the increasing adoption of outcome-driven metrics (ODMs) to an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. The frequency and negative impact of cyberattacks have seen organizations question their strategy and regularly test if it is being continuously improved upon.
To that end, ODMs create a clearer path between the investment in cybersecurity and the results it generates in the form of delivered protection levels, in language easily understood by non-IT executives. What’s interesting is that cybersecurity teams are now increasingly being evaluated during appraisals on these metrics.
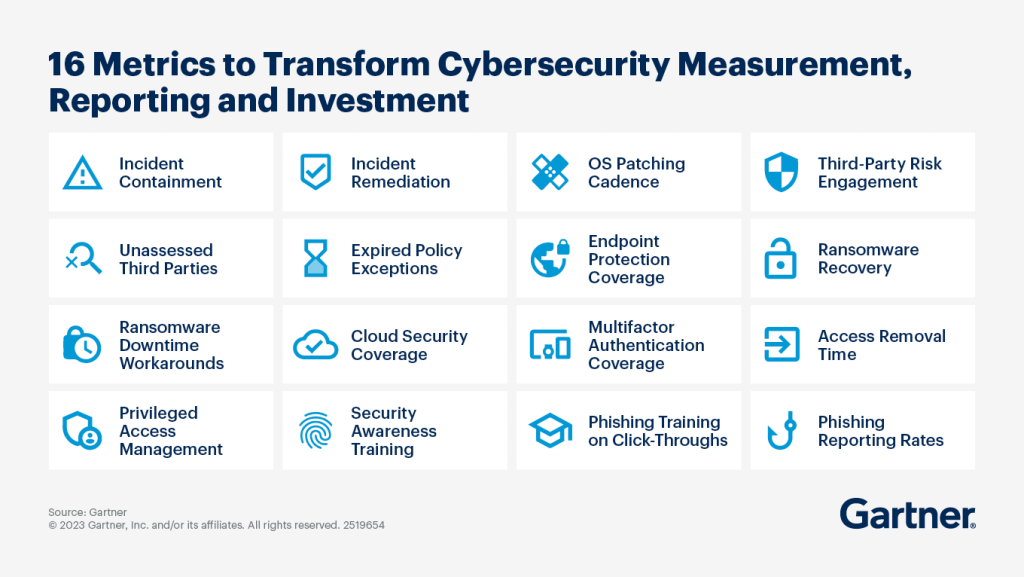
Gartner identifies 16 key metrics that are required for cybersecurity measurement, reporting, and investment.
Trend #3: SBCPs to Reduce Human Error
Gambling can sometimes be fun, but not when it comes to your customers’ private data. That’s exactly what happened when attackers from the group Scattered Spiders obtained MGM employee info on LinkedIn and impersonated them while speaking to MGM’s IT help desk to get credentials.
A ransomware attack ensued, MGM’s systems were completely shut down, and there were reports of malfunctioning slot machines and room keys, followed by a reveal a few days later that customer names, contact info, gender, DOB, and even Social Security Numbers, were leaked as part of the breach.
Don’t gamble with your organizational data like that. This breach wouldn’t have happened if MGM’s IT team had been sufficiently trained in ideal cybersecurity practices. The only way to avoid human error, which forms the basis of so many cyberattacks, is to have a focus shift from ‘increasing awareness’ amongst your employees to ‘fostering behavioral change’.
Effective security behavior & cultural programs (SBCPs) are crucial to achieving that leap. Through these programs, you can successfully create better employee adoption, reduce slack behavior, and thus increase speed & agility. Through the efficacy of these measures, employees become competent at making independent cyber risk decisions.
Read more on how Human Errors are the weakest link in the cybersecurity fabric, a POV by Mitish Chitnivas, CTO, iValue Group.
Trend #4: Resilience-Driven, Resource-Efficient TPRM
Third parties shouldn’t be your organizational crutch. Instead, by establishing mutually beneficial relationships with third parties that ensure that your most valuable assets are continuously safeguarded, they can be valuable assets.
The London Metropolitan Police found that out the hard way when its IT supplier, Digital ID, experienced a ransomware attack in August 2023.
Through this, sensitive information of nearly 47,000 law enforcement officers & staff was exposed. We’re talking names, photos, ranks, and identification numbers for all these officers. Seriously dangerous real-world ramifications possibly ensued when you consider that some officers were undercover or involved in counter-terrorism ops.
The key to choosing the latter is an enhanced third-party risk management (TPRM) strategy, that moves away from front-loaded due diligence activities to a strategy involving continuous monitoring and improvement. Some essentials your TPRM strategy should contain include:
- Incident playbooks
- Tabletop exercises
- A clear offboarding strategy, including timely revocation of access and destruction of data
Trend #5: Prominence of CTEM Programs
Ever played Call of Duty or World of Warcraft? If you have (or even if you haven’t), it would interest you to know that Activision, the company that develops these games, suffered a data breach last February. Well, the hack happened in December 2022, but they only found out about it the following February.
The attackers gained access through an SMS phishing attack on an HR employee who had access to sensitive employee information. They obtained full names, email IDs, phone numbers, salaries, work locations, and – get this – even sensitive details about upcoming content for their Call of Duty Modern Warfare 2 franchise.
The shocking part was, that this wasn’t disclosed for months until malware research group vx-underground shared a bunch of screenshots regarding the breach.
The chances of the Activision scenario arising in your organization dip drastically with a solid continuous threat exposure management (CTEM) program. It speaks volumes when Gartner says that by 2026, organizations prioritizing investment in CTEM programs will see a two-thirds reduction in breaches.
This program continuously monitors hybrid digital environments to enable early identification and optimal prioritization of vulnerabilities. These measures help maintain a solid organizational attack surface.
The key to doing this is aligning assessment & remediation scopes with threat vectors and individual projects instead of the entire infrastructure – essentially, focusing on the micro as a means of securing the macro.
Trend #6: Increasing Importance of IAM
The cybersecurity world is moving towards an identity-first security approach, and identity & access management (IAM) forms the crux of that.
Yet, even before the Activision incident, the tone for a concerning year was set in January 2023, when MailChimp reported that data had been compromised for over 133 of their corporate clients. One of those was WooCommerce, a popular e-commerce plugin for WordPress, who later informed users that the breach exposed names, store URLs, and email IDs. 133 business clients don’t sound that substantive until you consider just how much user data each of those clients holds.
So, how did it happen? Through a social engineering attack on MailChimp employees and contractors that enabled the attackers to obtain employee credentials. Through this, they accessed tools used by teams interacting with clients for customer service and account management.
To be fair to MailChimp, they detected the breach quickly, suspended access immediately, and informed the public less than 24 hours after the initial discovery.
Situations like the MailChimp breach don’t happen with a strong identity fabric and quick threat detection & response tools being the pillar of your IAM. Zero trust is also becoming an increasingly adopted tenet moving forward.
So, there we have it, Gartner’s 6 cybersecurity trends for 2024 becoming all the more heightened due to relevant cautionary tales from the previous year. Thank you for reading, and stay cybersafe!
